
Java programmer expert
Today we will take a look at another Java design pattern from the category of patterns for creating objects (creational patterns) – Prototype.
V článku sa dozvieš:
Read more about other design patterns:
The Prototype design pattern is a software design pattern used to create new objects by copying an existing object.
It solves the problem of creating new objects with minimal cost in computing time and memory by avoiding the repeated creation of objects using the constructor. Instead, we create an example instance (prototype) that we can then copy when we need to create a new object.
This design pattern is useful when object creation is difficult, or when getting new instances of an object is different from simply calling its constructor. It is also useful for making deep copies of objects that contain complex data structures.
Now we will show you how to implement the Prototype pattern in Java.
Shape.java
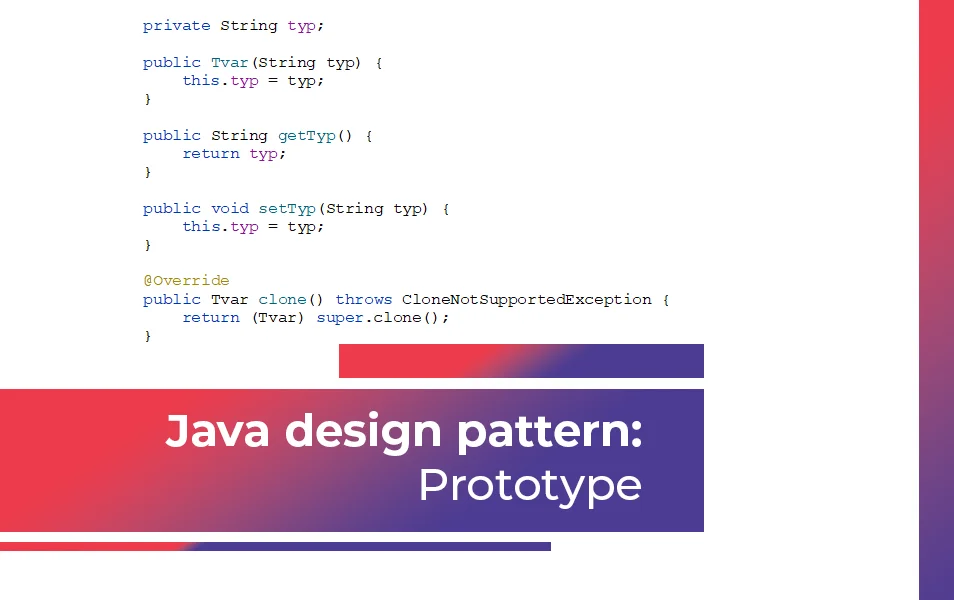
The shape class represents a Prototype pattern that needs to implement the Cloneable interface and overload the clone() method.
package designpatterns;
public class Shape implements Cloneable {
private String type;
public Shape(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
@Override
public Shape clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Shape) super.clone();
}
}Here is an example of using the Shape class with the Prototype design pattern implementation:
Main.java
In this example, we have created a Shape class, which represents a prototype object. In the main method, we first created a prototype instance of type Circle. We then copied this instance and created the Shape1 object. After changing the type of Shape1, we copied the pattern again and created the Shape2 object.
import designpatterns.Shape;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Shape creation
Shape prototype = new Shape("Circle");
try {
// Clone shape to create a new object
Shape shape1 = prototype.clone();
System.out.println("Object 1: " + shape1.getType());
// Changing the type of new object
shape1.setType("Square");
System.out.println("Object 1 after type change: " + shape1.getType());
// Creating another object by cloning the shape
Shape shape2 = prototype.clone();
System.out.println("Object 2: " + shape2.getType());
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}The output of this example should be like this:

We have prepared files with the above example prototype code that you can run directly in Java. Download the code here.
Related articles